Role of foreign capital in economic development
Definition
A
foreign direct investment (FDI) is a controlling ownership in business
enterprises in one country by an entity based in another country. In developing
countries like India It is an opportunity to make the Economy in a balance
Position or make if even better one. As it are playing as one of the growth
engines of an economy. FDI is now considered as a creator of Wealth through its
corporate sector and mobilize of much needed resources.
FDI
flows comprises capital provided by foreign investors, directly or indirectly
to enterprises in another economy with an expectation of obtaining profits
derived from the capital participation in the management of the enterprises in
which they invest.
Foreign Capital in India
Everywhere
in the world including the developed countries, governments are vying with each
other to attract foreign capital. The belief that foreign capital plays a
constructive role in a country’s economic development. It has become even
stronger since mid-1980.
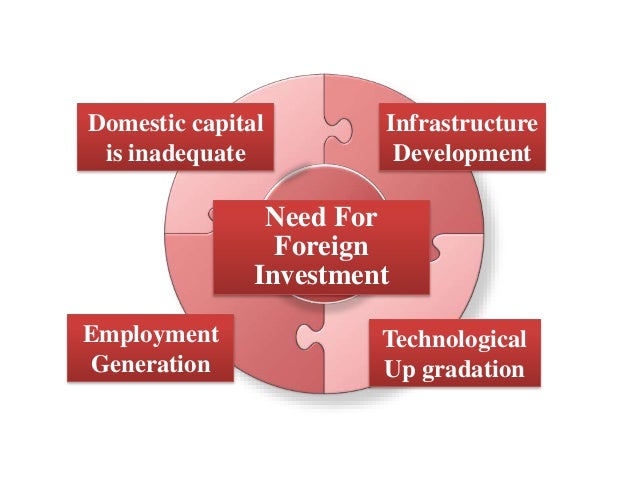
Need For Foreign Capital
The need for foreign capital arises because of the
following reasons.
- In most developing countries like India, domestic capital is inadequate for the purpose of economic growth. Foreign capital is typically seen as a way of filling in gaps between the domestically available supplies of saving, foreign exchange, government revenue and the planned investment necessary to achieve development targets.
- An inflow of private foreign capital helps in removing deficit in the balance of payments over time if the foreign-owned enterprises can generate a net positive flow of export earnings.
- The third gap that the foreign capital and specially, foreign investment helps to fill is that between governmental tax revenue and the locally raised taxes. By taxing the profits of the foreign enterprises the government of developing countries are able to mobilize funds for projects (like energy, infrastructure) that are badly needed for economic development.
- Foreign investment meets the gap in managements , entrepreneurship, technology and skill. The package of these much-needed resources is transferred to the local country through training programmes and the process of learning by doing.
- Further foreign companies bring with them sophisticated technological knowledge about production processes while transferring modern machinery equipment to the capital-poor developing countries.
In fact, in this era of globalization, there
is a great belief that foreign capital transforms the products structures of
the developing economic leading to high rates of growth. Besides the above
foreign capital, by creating new productive assets, contributes to the
generation of employment a prime need of a country like India
Reasons for Foreign Capital Inflows
- Capital investment requirement – Since underdeveloped countries want to industrialize themselves within a short period of time, it becomes necessary to increase capital investment substantially. This requires a high level of savings. However, because of general poverty, the savings are very low. This creates a resource gap between investment needs and savings. This gap has to be filled through foreign capital.
- Technology transfers – The under developed countries have lower technological capacity as compared to advanced countries. The desire for industrialization creates the need for improving technology from advanced countries. Such technology transfer usually comes with foreign capital in the form of private foreign investment or foreign collaboration. The technological gap is reduced by training domestic personal and through establishment of educational, research or training institutes.
- Exploitation of natural resources – A number of underdeveloped countries posses huge mineral resources, which can be exploited for economic development. These countries do not possess the required technical skill and expertise to accomplish this task. As a consequences, they have to depend upon foreign capital to undertake the exploitation of their mineral wealth.
- Development of entrepreneurship – Many under developed countries suffer from shortage of private entrepreneurs. This creates a limitation in the process of industrialization. Foreign capital undertakes the risk of investment in host countries and this provides the much-needed impetus to the process of industrialization. Once the process of industrialization gets started with foreign capital, domestic industrial activity also increases through greater local participation. This automatically develops local entrepreneurship.
- Development of economic infrastructure – The domestic capital in under developed countries is inadequate to build the required level of economic infra structure. Thus these countries require the assistance of foreign capital to undertake the task. Over the last 50 years, international financial institutions and governments of advanced countries have made substantial capital available to the under developed countries to develop their economic infrastructure in the form of transport and communication systems, generation and distribution of electricity, development of irrigation facilities etc. The basic intention is to build an economic model for achieving sustainable development.
- Financing balance of payments deficit – In the initial phase of economic development, under developed countries face larger imports (in the form of machinery, capital goods, industrial raw materials, spares and components), than exports. The deficit in the balance of trade is financed by inflow of foreign capital. The economic development of an underdeveloped country therefore needs foreign capital to initiate its economic development process and sustain it till desired level of stability is reached.
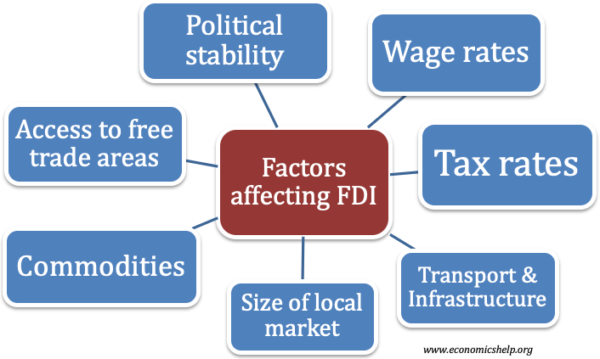
factors affecting FDI flow
SUGGESTIONS FOR INCREASED INFLOW OF FDI INTO
THE COUNTRY
1. FLEXIBLE
LABOUR LAWS NEEDED: China gets maximum FDI in the manufacturing
sector, which has helped the country become the manufacturing hub of the world.
In India the manufacturing sector can grow if infrastructure facilities are
improved and labour reforms take place. The country should take initiative to
adopt more flexible labour laws.
2. RE
LOOK AT SECTORAL CAPS: Though the Government has hiked the sectoral
cap for FDI over the years. It is time to revisit issues pertaining to limits
in such sectors as coal mining, insurance, real estate and retail trade, apart
from the small-scale sector. Government should allows more investment into the
country under automatic route. Reforms like bringing more sectors under the
automatic route, increasing the FDI cap and simplifying the procedural delays
has to be initiated. There is need to improve SEZs in terms of their size, road
and port connectivity, assured power supply and decentralized decision making.
3. GEOGRAPHICAL
DISPARITIES OF FDI SHOULD BE REMOVED: The issues of Geographical
disparities of FDI in India need to address on priority. Many states are making
serious efforts to simplify regulations for setting for setting up and operating
the industrial units. However, efforts by many state governments are still not
encouraging. Even the state like West Bengal which was once called Manchester
of India attract only 1.2% of FDI inflow in the country. West Bengal, Bihar,
Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh are endowed with rich minerals but due to lack of
proper initiatives by governments of these states, they fail to attract FDI.
4. PROMOTE
GREEFIELD PROJECTS: India’s volume of FDI has increased largely due to
Merger and Acquisitions (M&As) rather than large Greenfield projects.
M&As not necessarily imply infusion of new capital into a country if it is
through reinvested earnings and intra company loans. Business friendly
environment must be created on priority to attract largeGreenfield projects.
Regulations should be simplified so that realization ratio is improved
(Percentage of FDI approvals to actual flows). To maximize the benefits of FDI
persistently, India should also focus on developing human capital and
technology.
5. DEVELOP
DEBT MARKET: India has a well developed equity market but does not
have a well developed debt market. Steps should be taken to improve the depth
and liquidity of debt market as many companies may prefer leveraged investment
rather than investing their own cash. Therefore it is said that countries with
well-developed financial markets tend to benefits significantly from FDI
inflows.
6. EDUCATION
SECTOR SHOULD BE OPENDED TO FDI: India has a huge pool of working
population. However due to poor quality primary education and higher education,
there is still an acute shortage of talent. FDI in Education Sector is lesser
than one percent. By giving the status of primary and higher education in the
country, FDI in this sector must be encouraged. However, appropriate measure
must be taken to ensure quality education. The issues of commercialization of
education, regional gap and structural gap have to be addressed on priority.
7. STRENGTHEN
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN THE COUNTRY: India should consciously work
towards attracting greater FDI into R&D as a means of strengthening the
country’s technological powers and competitiveness.
pros and cons
CONCLUSION
FDI play an important role in the long-term development of a country not only as a source of capital but also for enhancing competitiveness of the domestic economy through transfer of technology, strengthening infrastructure, rising productivity and generating new employment opportunities. India emerges as the fifth largest recipient of foreign direct investment across the globe and second largest among all other developing countries (World Investment Report 2010). The huge market size, availability of highly skilled human resources, sound economic policy, abundant and diversified natural resources all these factors enable India to attract FDI.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/free-trade-agreement-pros-and-cons-3305845-final-5b71e37f46e0fb002cdbc389.png)


Comments
Post a Comment